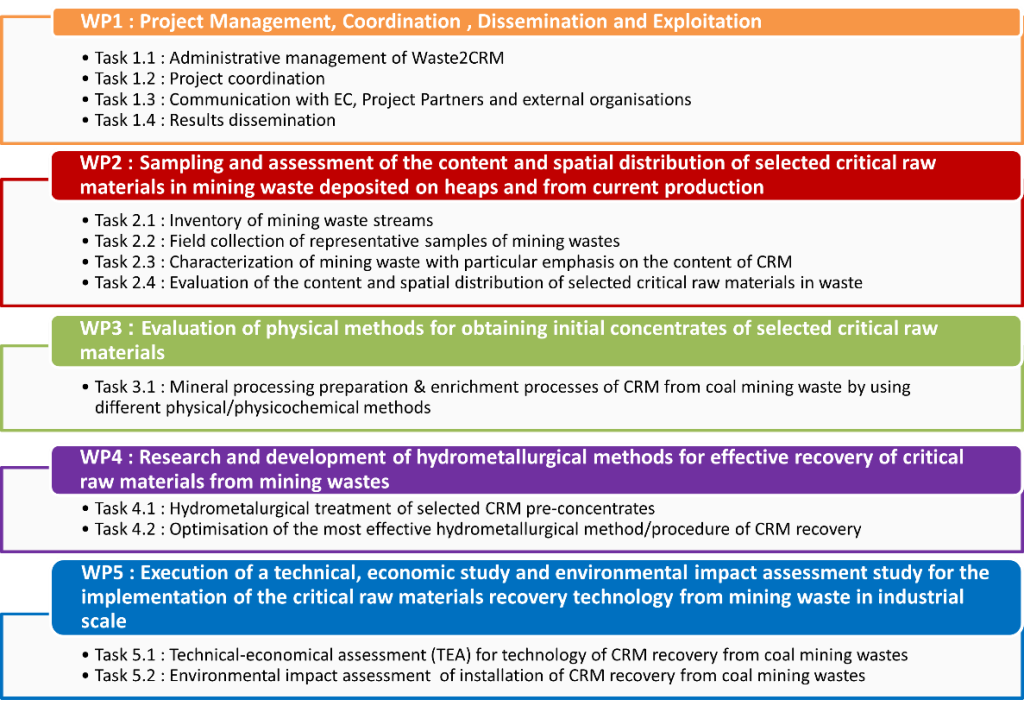
Work Package 1: Project Management, Coordination, Dissemination and Exploitation
- This work package is primarily administrative and focuses on project management, not direct R&D. However, it indirectly supports R&D by ensuring effective communication and resource allocation among the partners. Dissemination activities (reporting and publications) are considered a form of R&D output.
Work Package 2: Sampling and assessment of the content and spatial distribution of selected critical raw materials in mining waste deposited on heaps and from current production
- Inventory of mining waste streams: Compilation and analysis of existing databases on coal mining waste, identifying potential sources for critical raw materials (CRMs).
- Field collection of representative samples: Systematic sampling of coal mining waste from various locations (heaps, current production) to obtain representative samples for analysis.
- Characterization of mining waste: Detailed physicochemical and geochemical analyses of the collected samples to determine the concentration and distribution of CRMs, including rare earth elements (REEs).
- Evaluation of the content and spatial distribution: Statistical analysis of the analytical data to understand the distribution of CRMs within the waste deposits and identify optimal areas for further processing.
Work Package 3: Evaluation of physical methods for obtaining initial concentrates of selected critical raw materials
- Mineral processing: This is the core R&D of this work package, focusing on testing and optimizing various physical and physicochemical separation techniques (crushing, grinding, gravity separation, magnetic separation, electrostatic separation, sensor-based sorting, froth flotation) to enrich the CRM content in the waste material..
Work Package 4: Research and development of hydrometallurgical methods for effective recovery of critical raw materials from mining wastes
- Hydrometallurgical treatment of pre-concentrates: This is the core R&D, testing various hydrometallurgical methods (acid leaching, alkaline leaching, ion exchange, etc.) on the CRM-enriched concentrates from WP3 to determine the optimal conditions for effective CRM recovery. This also involves investigating pre-treatment steps (e.g., calcination, microwave treatment) to enhance recovery.
- Optimization of the most effective hydrometallurgical method: Refinement and optimization of the most promising hydrometallurgical method, aiming for maximum recovery and efficiency.
Work Package 5: Execution of a technical, economic study and environmental impact assessment study for the implementation of the critical raw materials recovery technology from mining waste in industrial scale
- Technical-economic assessment (TEA): This is not direct laboratory R&D, but rather an economic and engineering feasibility study, assessing the costs and potential profits of implementing the developed CRM recovery technology on an industrial scale.
- Environmental impact assessment (LCA): A Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) will be conducted to evaluate the environmental impacts of the entire CRM recovery process, from waste extraction to final product disposal.